Blockchain technology, a revolutionary invention in the realm of digital transactions, has garnered a significant amount of attention in recent years. Despite its popularity, the concept of Blockchain remains shrouded in mystery for many. Together we’ll take a small step into the world of blockchain technology by dissecting its structure, functionality, and potential applications.
The Basics of Blockchain
Blockchain is a digital ledger, a record book, that records transactions. It’s like a collection of accounts where transactions are recorded. Each block is connected to the blocks before and after it, creating a chain. This makes it difficult to tamper with a single record. Blockchain technology operates on a decentralised platform, ensuring the absence of a central authority and providing an environment that fosters transparency, security, and credibility.
Blockchain: A Distributed Ledger
At its core, Blockchain is a type of distributed database or ledger, a concept that stands as one of the top technology trends of the 21st century. Unlike traditional databases managed by a central system, the control and management of a blockchain database are distributed among a network of computers known as nodes. This decentralised structure, termed as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), plays a crucial role in enhancing the security and credibility of data stored within the Blockchain.

The term “blockchain” is derived from the way data is stored within the system. Each “block” in a blockchain represents a digital record of transactions. When a block is filled to its capacity, it is linked to the preceding block, forming a chain of data. The connection between blocks is established using cryptographic hashes, creating an immutable chain that is nearly impossible to alter or tamper with.
Decentralisation: The Heart of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is distinguished by its decentralised nature, which means that it is not controlled by a single entity or authority. Rather than data being stored on a single server or database, copies of the Blockchain are distributed across numerous devices or nodes. This distribution not only ensures data redundancy but also maintains the integrity of the data.
Blockchain at Work: A Step-by-step Breakdown
Understanding the operational mechanism of blockchain technology can be a complex task. However, by breaking down the process into discrete steps, one can gain a clearer picture of how blockchain functions.
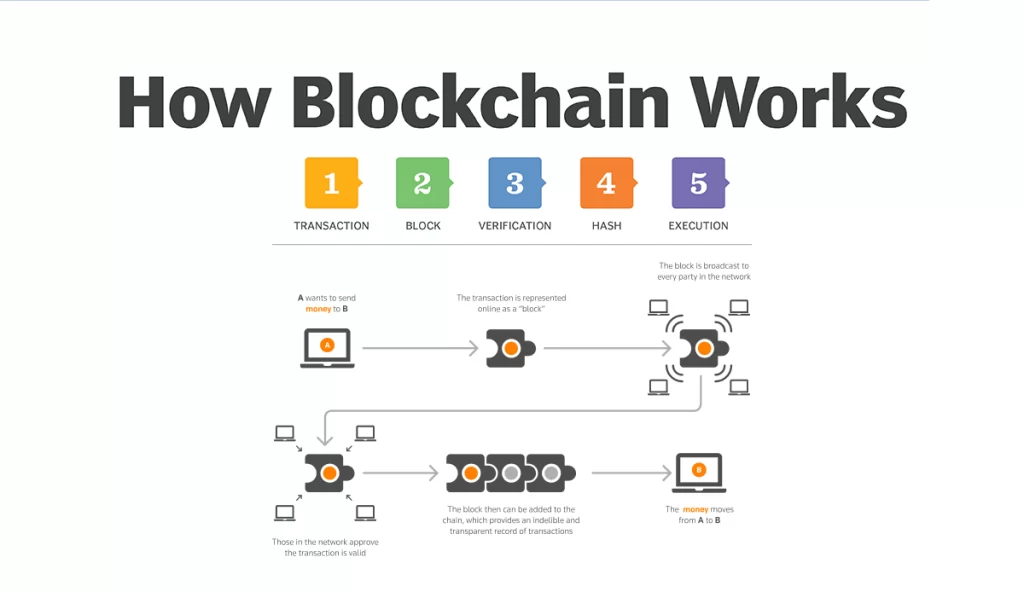
- Recording Transactions
The first step in a blockchain is recording a transaction. When a transaction is sent, it is grouped with other transactions that have occurred in close proximity to each other. This group of transactions forms a “block” of data.
- Block Verification
After a block is created, it needs to be checked by a network of computers, known as nodes, in the Blockchain. This verification process is done by the nodes to ensure that the transactions in the block follow specific rules. This helps ensure that only valid transactions are added to the Blockchain.
- Block Addition
After a block has been verified, it is added to the Blockchain. Each block is connected to the block before it, creating a chain of blocks. The addition of a new block to the Blockchain necessitates the update of every copy of the Blockchain across the network.
- Transaction Completion
The final step is the completion of the transaction. Once a block is added to the Blockchain, the transaction it contains is considered complete. The decentralised nature of the Blockchain ensures that the transaction is permanently recorded and cannot be altered.
Types of Blockchain: Public vs Private
Blockchain technology can be categorised into two primary types: public blockchains and private blockchains.
- Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are available to anyone who wants to participate. They have a set of rules that determine how new blocks are created and how transactions are validated. Bitcoin, the first and most popular cryptocurrency, runs on a public blockchain.
- Private Blockchain
In contrast, private blockchains are only accessible to a specific group of individuals or organisations. They are typically used within a single organisation or among a consortium of trusted participants. These blockchains can be customised according to the needs of the participating entities.
Key Elements of Blockchain Technology
Several key components play an essential role in the operation of a blockchain.
- Cryptography
In Blockchain, Cryptography is used to protect transactions and control the creation of new coins. It involves encrypting and decrypting data through complex mathematical algorithms.
- Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure all nodes in the blockchain network agree on the state of the shared ledger. These mechanisms are very important for maintaining the integrity and security of the Blockchain.
- Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executed computer programs that automatically carry out assignments when certain conditions are met. They are self-executing, meaning they don’t require human intervention to complete the task. Smart contracts can potentially help reduce the risk of fraud or mistakes since they automatically execute the tasks they were programmed to perform.
A good example to help understand this is a vending machine. When a customer inputs $2 and selects B4, the vending machine dispenses the cookies from the B4 slot. In other words, the vending machine performs an action when it receives the necessary payment or input. This is similar to what a smart contract does, but instead of cookies, it carries out a task or agreement.
Smart contract technology has enabled decentralised finance (DeFi), which is often associated with peer-to-peer transactions using cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum’s Ether. DeFi smart contracts can reduce the time and cost of settling these transactions. They also have the potential to automate manual banking processes traditionally performed by financial institutions, such as evaluating loan eligibility and processing insurance claims.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: An Inseparable Duo
The most common application of blockchain technology is in the realm of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin operate on a blockchain framework, allowing secure, peer-to-peer transactions to take place over the Internet.
- Bitcoin and Blockchain: The Original Pair
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. It marked the beginning of blockchain technology in the mainstream, which is a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions.
- Beyond Bitcoin: The Advent of Altcoins
Following the success of Bitcoin, numerous other cryptocurrencies, collectively known as altcoins (alternative coins), have been created. These altcoins, which include Ethereum, Litecoin, and Ripple, among others, operate on their own unique blockchains and offer different features and functionalities.
Potential Applications of Blockchain Technology
While cryptocurrency is the most common use case of blockchain technology, its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies.
- Banking and Financial Services
Blockchain technology has immense potential to revolutionise the banking and financial services sectors. From faster and more efficient money transfers to enhanced security and transparency, Blockchain offers numerous benefits to financial institutions.
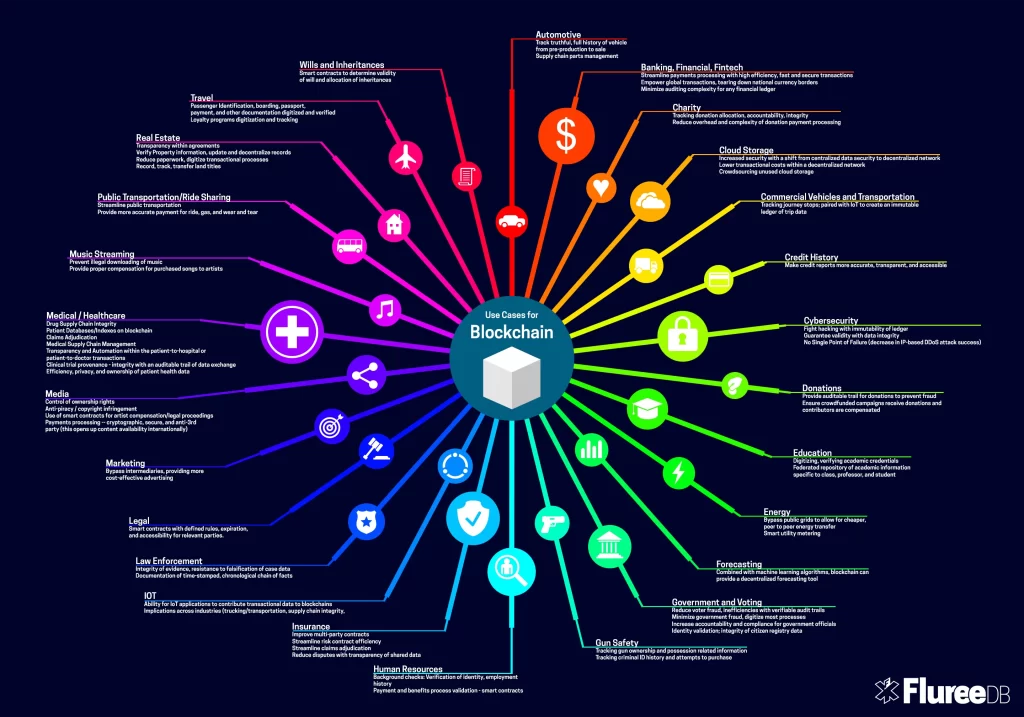
- Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can also be utilised to enhance supply chain management processes. By recording every transaction and movement of goods in a transparent and immutable ledger, Blockchain can help improve traceability, reduce fraud, and enhance efficiency in supply chains.
- Healthcare
One of the Blockchain technology use cases in healthcare is to generate secure and unchangeable records of patient data, which can significantly enhance patient privacy and data security. Healthcare providers can easily share these records, improving the coordination of care and patient outcomes.
Research from Johns Hopkins University in 2016 found that poorly coordinated care is the third leading cause of death in the US, resulting in medical errors such as incomplete actions and errors in patient records. One way to improve this would be to create a blockchain-based system for medical records that can connect with existing electronic medical record software, providing a comprehensive, centralized view of a patient’s record.
- Voting Systems
Blockchain technology can be used to create voting systems that are secure and transparent. The process involves recording votes in an unchangeable ledger, which helps prevent electoral fraud and improves transparency. By using Blockchain, we can create a better voting process that is fair and trustworthy.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The ongoing research and development efforts exploring new and innovative applications of blockchain technology promise a bright future.
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Blockchain technology has become more accessible with the introduction of Blockchain as a Service (BaaS). BaaS is a cloud-based service that simplifies blockchain application creation, usage, and hosting without the need for infrastructure management. This is very useful for individuals or businesses who want to use blockchain technology but lack the expertise or resources to maintain the infrastructure. BaaS enables anyone to take advantage of blockchain technology without needing technical expertise.
- Interoperability of Blockchain Networks
Another promising development in the blockchain space is the increasing interoperability of different blockchain networks. This will allow different blockchain networks to interact and transact with each other, opening up new possibilities for collaboration and data sharing.
Challenges and Concerns About Blockchain Technology
While the potential of blockchain technology is undeniable, there are several challenges and concerns that need to be addressed.
- Scalability
Blockchain technology has a problem with scalability. When there are a lot of transactions on a blockchain, it takes more time and computing power to process and verify each one. This can cause transactions to take longer and cost more, which could discourage people from using blockchain technology.
- Energy Consumption
There is growing concern about the amount of energy used by blockchain technology, specifically public blockchains that use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms. Mining requires a lot of energy. This energy consumption is a major issue.
One of the reasons for this issue is the computational power required for mining. This process requires a lot of energy and computational power, which can be harmful to the environment. Additionally, public blockchains that use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms can be slower and less efficient than other types of blockchains.
To address this issue, different consensus mechanisms have been proposed, which require less energy. These mechanisms include proof-of-stake and proof-of-authority. By using these mechanisms, the energy consumption of blockchain technology can be reduced, while still maintaining the security and decentralization of the blockchain.
- Regulatory and Legal Issues
Lastly, there are several regulatory and legal issues associated with blockchain technology. Since Blockchain operates in a decentralised manner, it can be challenging to regulate and oversee. Furthermore, the use of Blockchain for illegal activities, such as money laundering or fraud, poses significant legal challenges.
Blockchain and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Blockchain technology has been used to create non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs are special digital assets that use blockchain to keep them unique. They are used to prove ownership or authenticity of digital or physical property, like digital art, music, or even real estate. NFTs are popular for investment and have become a new trend in the world of digital art and culture.

CryptoPunk #5822, an alien-style punk with a blue bandana, sold for a record-breaking $23 million on February 12th, 2022
Source: Larva Labs
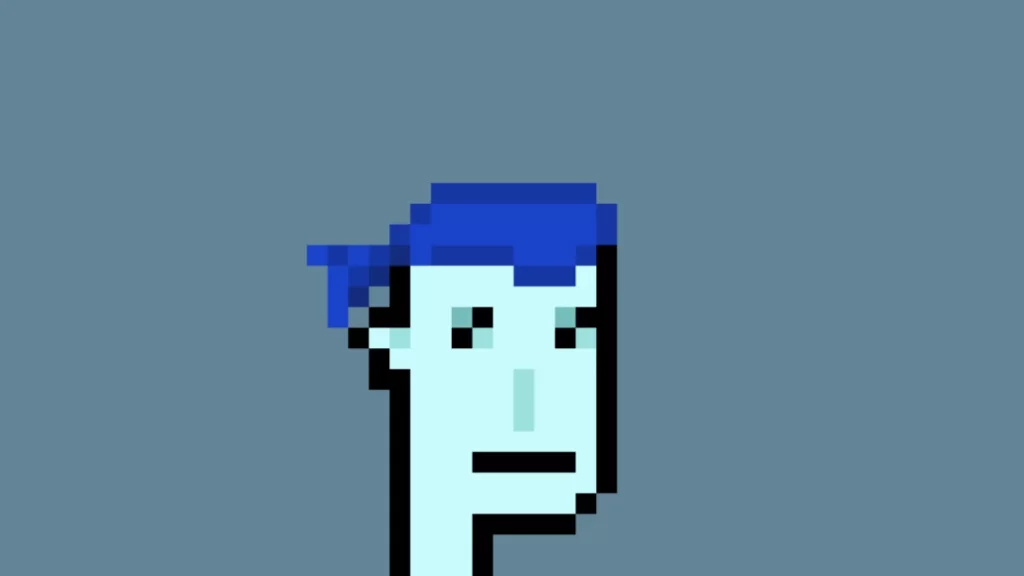

Source: Larva Labs
Investing in Blockchain Technology
While it is not possible to invest directly in blockchain technology, there are several ways to gain exposure to this revolutionary technology. One can invest in cryptocurrencies that operate on a blockchain, purchase stocks of companies that are developing or using blockchain technology or invest in blockchain-focused exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Blockchain Security: A Double-Edged Sword
While Blockchain is often hailed for its superior security, it’s important to note that no technology is completely foolproof. The decentralised nature of Blockchain, coupled with its reliance on cryptography, makes it a formidable barrier against hacks and fraudulent activities. However, the system is only as secure as its weakest link. If a user loses their private cryptographic key, the digital assets associated with that key are lost forever. Moreover, Blockchain’s anonymity and privacy features could potentially be exploited for illicit activities.
FAQ
What is the blockchain in simple terms?
Blockchain is a digital ledger, a record book, that records transactions. It’s like a collection of accounts where transactions are recorded
Why use blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology can improve business operations by enhancing trust, security, transparency, and traceability of shared data, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency.
Where is blockchain used?
Government, healthcare, real estate industry and more.
What is an example of a blockchain technology?
Amazon Retail has filed a patent application for a blockchain-based system to verify the authenticity of all products sold on their platform.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Despite the challenges, there is a future for blockchain technology and it appears to be bright. Its potential to revolutionise various sectors, from finance to healthcare, is immense. As more research is conducted and more advancements are made, the applications of Blockchain will likely become more diverse and its adoption more widespread.
However, for blockchain technology to reach full potential, ongoing collaboration among developers, businesses, regulatory bodies, and consumers is crucial. Only through such collaborative efforts can the challenges be adequately addressed and the benefits of blockchain technology be fully realised.
In conclusion, blockchain technology, with its unique combination of decentralisation, security, and transparency, presents a paradigm shift in the way we conduct digital transactions. As we continue to explore and utilize this groundbreaking technology, we’re excited to see how it will shape our digital future.





