In the digital age, smart contracts have emerged as a disruptive technology, revolutionising the way transactions are conducted. No longer do we need to rely on intermediaries – smart contracts offer an efficient, transparent, and secure alternative. But what are these digital contracts, and how do they work?
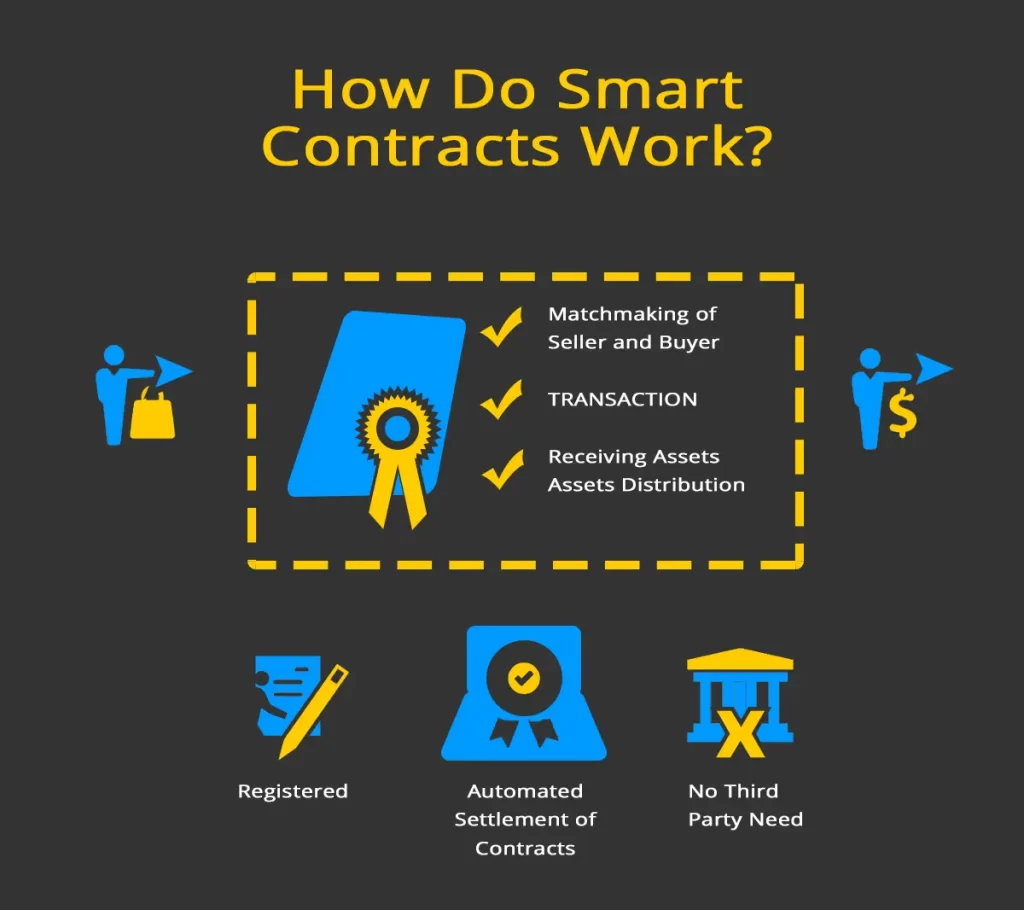
Understanding the Concept of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are digitaly signed contracts on the blockchain. They are written in code and can execute themselves. They remove the need for a third party to help with the negotiation or execution of a contract. By eliminating third parties, smart contracts make the process more efficient and secure.
The Mechanism Behind Smart Contracts
Smart contracts may seem complex, but their workings can be broken down into six steps:
- Agreement on Terms and Conditions – Just like traditional contracts, smart contracts also kick off with an agreement. The sides involved must agree on the terms and conditions, which will then be coded into the smart contract.
- Creation of the Smart Contract – Once the terms are agreed upon, the smart contract is created. This could be done by the parties themselves or by a developer. The coding of the contract includes the rules and consequences, similar to a conventional contract.
- Deployment of the Smart Contract – The next step is to place the smart contract to a blockchain. Once the transaction is confirmed, the contract goes live and cannot be changed or revoked.
- Meeting the Trigger Conditions – A smart contract monitors the blockchain or other digital sources for certain conditions or triggers. Once these conditions are met, the contract is ready to execute.
- Execution of the Smart Contract – Smart contracts operate automatically when certain conditions are met. These conditions can trigger actions like transferring funds or registering assets, like NFTs.
- Recording the Contract Result – The execution of the contract is broadcast to the blockchain, verified, and recorded as a transaction. The completed contract is stored on the blockchain and is available for review.
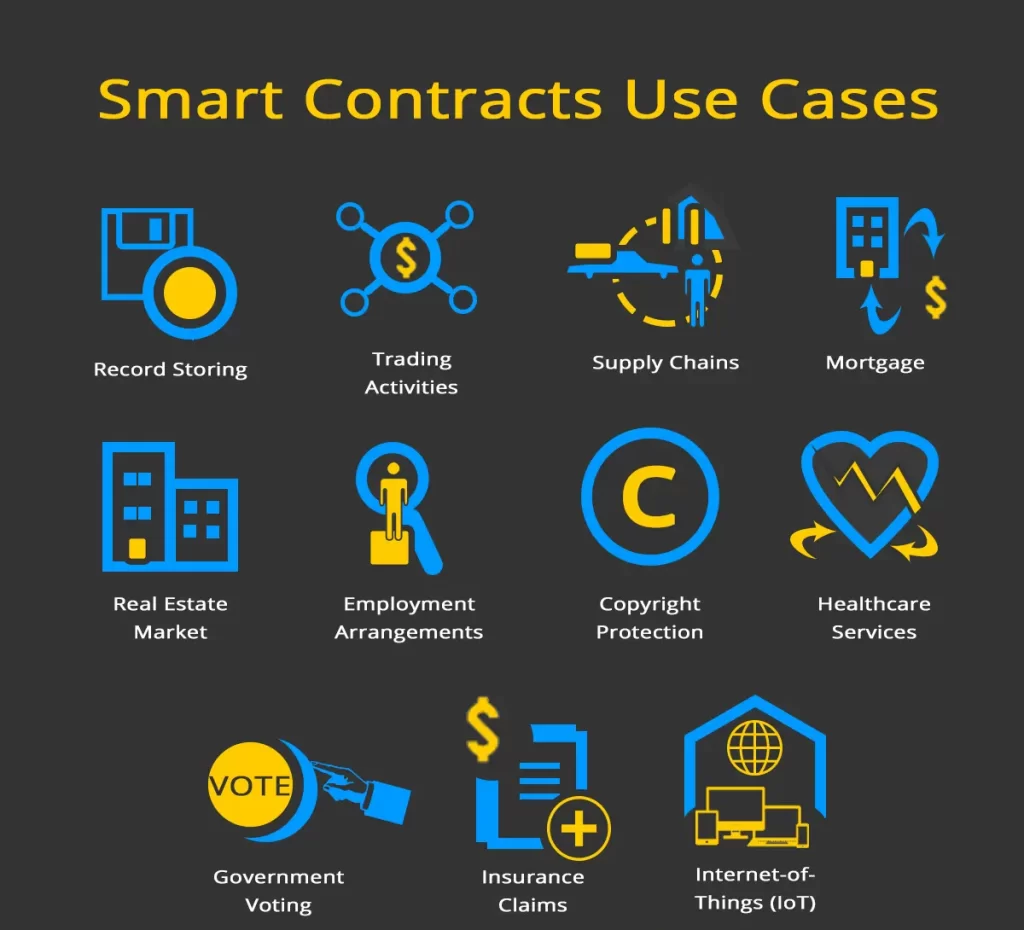
Potential Applications of Smart Contracts
The versatility of smart contracts allows them to be used in a variety of contexts:
- Automatic Savings: Smart contracts can automate savings by moving money into a designated account every month.
- Automatic Investing: They can automate investing activities, making buy and sell decisions based on the coded conditions. This niche is called DeFi and is happening mainly on the Ethereum blockchain network
- Insurance Claims: Smart contracts can expedite insurance claim processes by paying out immediately when certain verifiable events occur.
- Estate Planning: They can be added to an estate plan to automatically distribute digital assets upon a person’s death, potentially eliminating the need for probate court.
Are Smart Contracts Secure?
While smart contracts replace trust in humans with trust in code, they are not without risks. Coding errors, network congestion, expensive transaction fees, and legal enforceability are just a few of the potential risks. Developers, therefore, need to ensure rigorous testing, regular audits, performance verification, security features, and legal binding during the development process.
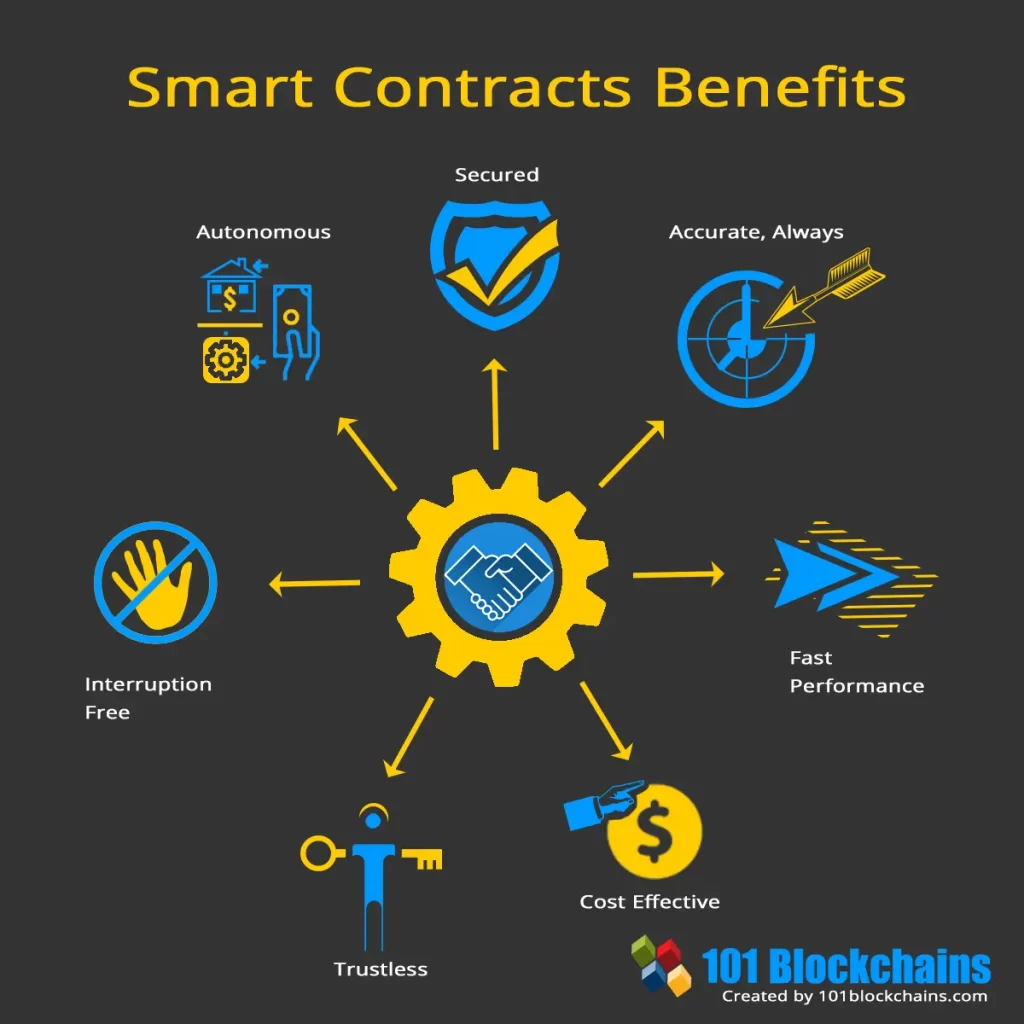
Smart contracts offer a promising new way to conduct transactions, automating processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries. However, just like any technology, they come with their own set of challenges and risks. As they continue to evolve, we can anticipate a future where smart contracts become a norm in our digital transactions, encouraging an era of trustless systems.
FAQ
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is, as name implieds, a digital contract that runs on the blockchain and follows a set of rules written in code. The contract executes itself automatically, without needing a third party to enforce it.
How does a smart contract work?
A smart contract works in six steps – agreement on terms and conditions, creation of the smart contract, deployment to a blockchain, meeting the trigger conditions, execution of the contract, and recording the contract result.
What are the uses of smart contracts?
Smart contracts can be used for automatic savings, automatic investing, expediting insurance claims, and estate planning, among other things.
Are smart contracts secure?
While smart contracts replace trust in humans with trust in code, they are not without risks. Developers must ensure rigorous testing, regular audits, performance verification in all possible environments, and legal binding during the development process.





